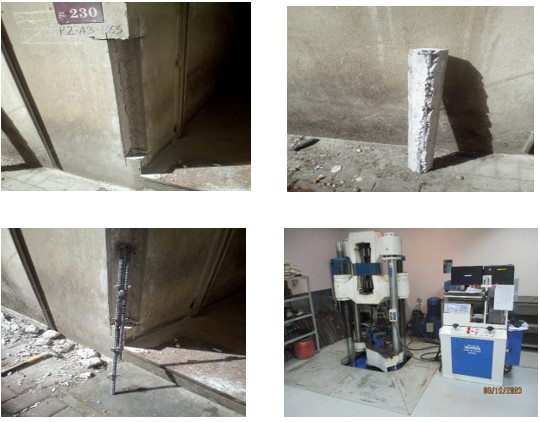
STEEL REBAR TEST
the scope of the test is according to,
2.1.BS 4449-2005:2016 specifies LIMITS for Tensile Strength, Yield Strength, Elongation, and Reduction of Area.
2.2.BS EN ISO 15630-1:2010 specifies test methods applicable to reinforcing bars, wires rods, and wire for concrete.
2.3.ISO 6892-1-2016 This part of the ISO 6892-1:2016 standard specifies the method for tensile testing of metallic materials and defines mechanical properties, which can be determined at room temperature.
2.1.BS 4449-2005:2016 specifies LIMITS for Tensile Strength, Yield Strength, Elongation, and Reduction of Area.
2.2.BS EN ISO 15630-1:2010 specifies test methods applicable to reinforcing bars, wires rods, and wire for concrete.
2.3.ISO 6892-1-2016 This part of the ISO 6892-1:2016 standard specifies the method for tensile testing of metallic materials and defines mechanical properties, which can be determined at room temperature.

EQUIPMENT TO BE USED
- Universal Testing Machine
- Digital Balance
- Steel Ruler
- Marker
- Drying Oven
PROCEDURE
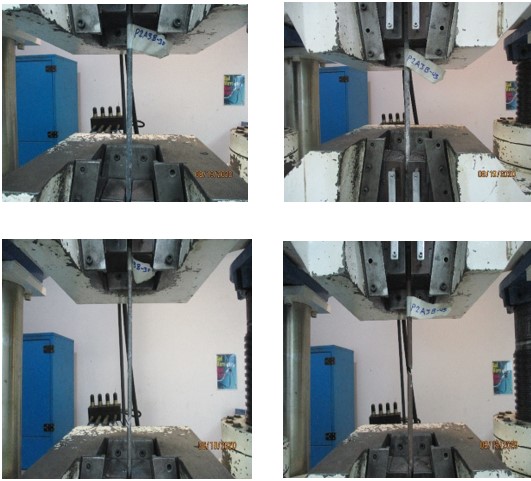
4.1.TENSILE TEST
The test involves straining a test piece by tensile force,
generally to fracture, to determine tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation test. According to ISO 15630-1; the 2010 test procedure shall be carried out in accordance with ISO
6892-1:2016. Testing rate based on stress rate (Method B) as per ISO 6892-1:2016(CL10.4)
(Table 3)
4.1.1.Calculation of Tensile Strength
For the calculation of tensile properties (ReH or Rp0,2, Rm), the nominal cross-sectional area shall be used.
4.1.2. (Using Nominal Cross Section Area Define In ANNEX D(D4)
Maximum Force(kN)/Nominal Cross-Sectional Area(mm²)x1000
4.2.YIELD STRENGTH
When the metallic material exhibits a yield phenomenon, stress corresponds to the point reached during the test at which plastic deformation occurs without any increase in the force. Testing rate based on stress rate (Method B) as per ISO 6892-1:2016(CL10.4) (Table 3)
4.2.1.Calculation of Yield Strength
For the calculation of tensile properties (ReH or Rp0,2, Rm), the nominal cross-sectional area shall be used, unless otherwise specified in the relevant product standard. ISO 15630-1:2010(CL5.3)
4.2.2.(Using Nominal Cross Section Area Define In ANNEX D(D4)
Yield Load(kN)/Nominal Cross-Sectional Area(mm²)x1000
4.3.TOTAL ELONGATION AT MAXIMUM FORCE(AGT)
For the determination of the total percentage elongation at maximum
force (Agt), ISO 6892-1 shall be applied with the following
modification:
⎯if Agt is determined by the
manual method after fracture, Agt shall be calculated from the following
formula:
Agt =Ag +Rm / 2 000
where Ag is the percentage of non-proportional elongation at maximum force. The measurement of Ag shall be made on the longer of the two broken parts of the test piece on a gauge length of 100 mm, as close as possible to the fracture but at a distance, r2, of at least 50 mm or 2d (whichever is the greater) away from the fracture. This measurement may be considered invalid if the distance, r1, between the grips and the gauge length is less than 20 mm or d (whichever is greater).
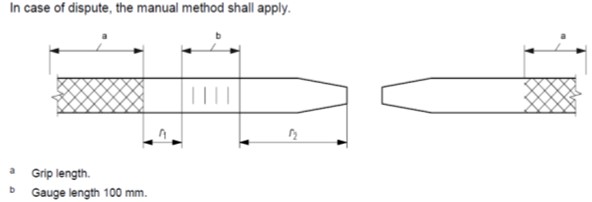
4.4.MARKING THE SPECIMEN FOR PERCENTAGE TOTAL ELONGATION AT MAXIMUM FORCE
If the total percentage elongation at maximum force (Agt) is
determined by the manual method, equidistant marks shall be made on the free
length of the test piece (see ISO 6892-1). The distance between the marks shall
be 20 mm, 10 mm, or 5 mm, depending on the test piece diameter.
If the total percentage elongation at maximum force (Agt) is determined by the manual method, equidistant marks shall be made on the free length of the test piece
(see ISO 6892-1).

