1.
Building Description
The building
under study is located at the intersection of ----------- Street.
The building
consists of the ground floor and five typical floors. The building is used as
workers' accommodation.
The
structure is made of conventional concrete slabs supported by beams that
transfer the loads to the columns, and the latter transfer the loads to the
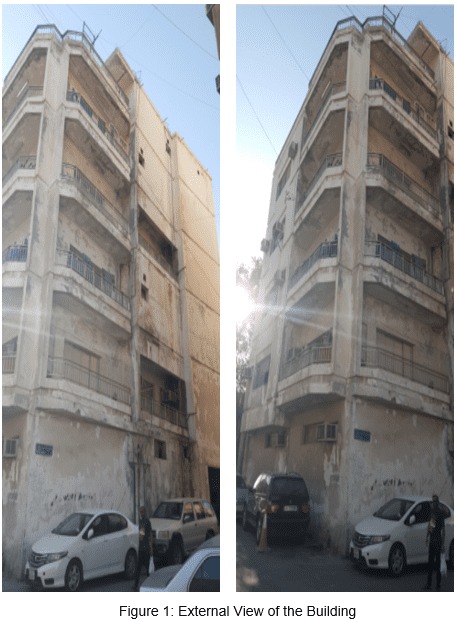
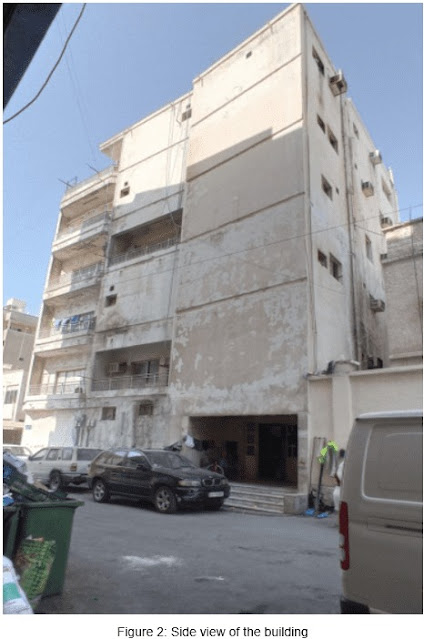
strata through footings. Figure 1 and figure 2 illustrate the building from
different angles.


2.
Visual inspection
During
the physical observation, all floor levels were inspected, and considerable
areas were exposed and checked, and a general assessment was conducted.
Investigation for various signs of deterioration was conducted, such as cracks'
patterns, spalling and delamination of concrete, honeycombs, discoloration,
etc. Also, a check for excessive deflection and distress, such as flexural and
shear cracks, was carried out.
The physical observations made during the inspection are summarized below, and figures from 3 to 9 present part of the visual observation.
1.
The structure of the building is moderately
deteriorated
2.
Various temperature and shrinkage cracks were
observed all over the building.
3.
Corrosion cracks were observed. Also, a trail
of corrosion was noticed.
4.
Concrete cover spalling and exposure of
reinforcement was observed in many places
5.
A lot of exposed reinforcement bars have
experienced a size reduction due to corrosion.
6.
Concrete delamination and paint peeling were
observed all over the building.
7.
Vertical cracks between concrete columns and
blockwork were observed in various places.
8.
Horizontal cracks were observed in balconies
9.
Diagonal cracks were noticed in some walls.
10.
Signs of water leakage were observed in many
places
11.
Trails of humidity and mold due to humidity and
water leakage were noticed.
12.
The roof's waterproofing system is damaged.

13. Conducted Tests
Tests, mainly,
were conducted on the columns since they are the critical structural element in
the building. The following tests were conducted:
1.
Carry out ultrasonic Pulse velocity test as per
EN 12504-4:2004.
2.
Obtain concrete cores from different locations
of the building to assess the physical and mechanical properties of the
existing concrete, according to EN 12504-1:2009.
3.
Measure the carbonation depth of concrete
elements by using phenolphthalein indicator according to BS 1881-201:1986 and
BS EN 14630.
4.
Extract reinforcement steel sample for a
tensile test following ASTM A370 or ISO 15630-1.
5.
Tests Results
The
following shows the results of the tests conducted. Table 1 summarizes the
conducted tests' results.
1.
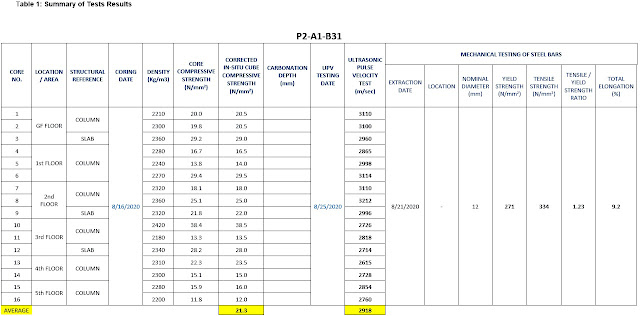
Ultrasonic test
The ultrasonic test was conducted on
several concrete elements to examine the quality of the concrete in general. Thirteen
columns and three slabs were tested. The results values were varying between 2615
m/s and 3212 m/s, which means that concrete condition varies between poor and
questionable condition.
2.
Compressive strength
and carbonation test
Sixteen concrete
cores were extracted, thirteen cores from the columns, and three cores from the
slabs.
Core compressive strength test results vary
between 12 MPa and 38.5 MPa for columns. As for the slab, the compressive
strength varies between 22 MPa and 29 MPa.
3.
Carbonation
No
carbonation was observed in the extracted samples.
4.
Tensile Test
One
specimen was extracted from a column to know the yield strength of the
reinforcement steel used in the structural elements. The yield strength of the
deformed bar was found to be 271 MPa
5.
Discussion of the Visual Inspection and
the Tests Results
From the physical investigation conducted, the
tests' results obtained, and the experience with similar buildings, most of the
observed cracks are the expected output due to the bad quality of work, lack of
regular and preventive maintenance, and the effect of variation in temperature
and humidity.
By applying
standard deviation to the Ultrasound tests' results, the average ultrasound
velocity was 2830 m/s, which means the quality of concrete is questionable. This conclusion was confirmed by the
compressive test results obtained, where the average concrete strength was 20.5
MPa.
Some of the tested columns had shown very low
strength values, e.g., 12 MPa. The low compressive strength of the concrete
elements combined with the effect of the numerous cracks in these elements and
the reduction in reinforcement diameter adversely affects the strength of these
elements. It could lead to the redistribution of the
stresses within the building, and that may cause failure or excessive
deformation in some building's elements.
Vertical cracks between the concrete
columns and the blockwork walls are due to temperature shrinkage. Some of the
observed diagonal cracks are related to the shrinkage effect. At the same time,
some others are related to the deflection in the supporting elements.
Horizontal cracks between the tiles
finishing layer and the slab are due to temperature variation.
Although the building
is not old, the bad quality control of the work during the construction period had
promoted the corrosion to initiate at an early stage and propagate.
6.
Conclusion
From the preceding observation and tests' results, the structural condition is considered poor. From the various inspected locations, one can assert that corrosion of the reinforcement steel has been propagating in many places in the building, and the deterioration is increasing, and spalling of concrete in many places will occur. The structural condition could be considered moderate, and more than 50% of the structural elements in the building require rehabilitation and strengthening.